
Cs04
White enamel | Density Calibration | Veil effect | White / black enamel | Interior perception
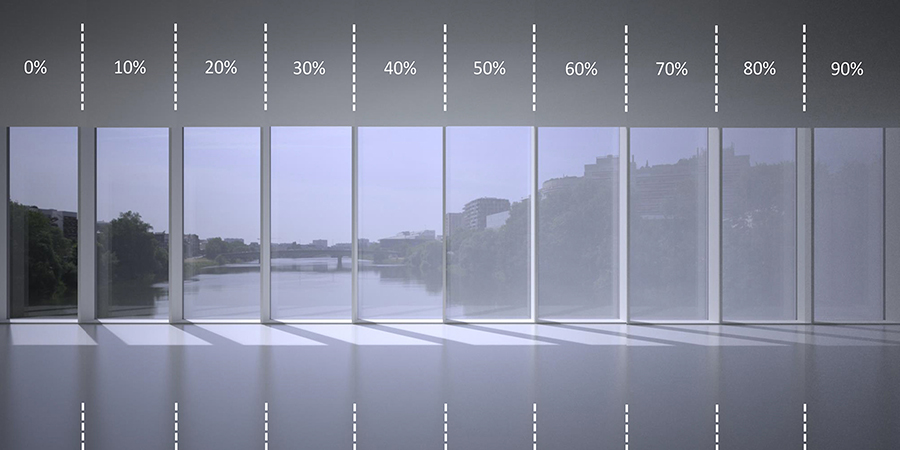
In this case study, we first look at various density of white enamel viewed from inside the building .
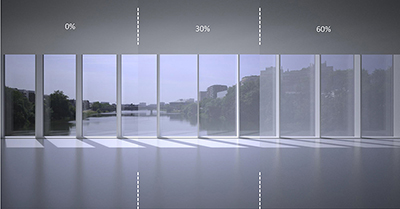
Fig A | white | 0% 30% 60%

.

Fig B | white | 30% 60% 90% | Blue sky

Fig C | white | 30% | Scattered + Blue sky
It shows on a phenomenon called the Veil effect which occurs when the dots are not perceived by the eye anymore due to a phenomenon called the eye fusion It occurs at a various distance depending on the dot size (with a dot or hole pattern) The pattern is then perceived as a continuous surface create appearance of a veil.
With White, as the density of enamel is getting greater, the veil appears more and more solid and reduces the see through transparency.

Fig D | white | 30% | In Out View | Blue sky

Fig G | Black – White | 90% | Out View | Blue sky
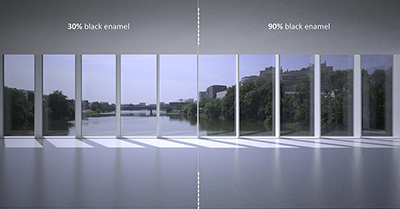
Fig I | Black | 30% + 90% | In View | Blue sky

Fig L | White | 30% 60% 90% | Out View

Fig E | white | 50% | In Out View | Blue sky

Fig H | Black-White | 90% | In View | Blue sky

Fig K | Black+White | 50% | In View | Blue sky

Fig M | Black | 30% 60% 90% | Out View

Fig F | white | 90% | In Out View | Blue sky
With white, the Veil will also be more or less strong depending of the light condition (Fig C). To avoid this veil effect, some product propose a dual deposit black toward the inside and white toward the outside. With black, the veil effect is almost totally avoided.
Fig M shows a self-moiré effect. The dot pattern place on the outer pane self reflects on the inner pane of the IGU. It was also presents with the white enamel but much more difficult to perceive on fixed image with such a low contrast . The black pattern brings enough contrast to make the moiré visible even on fixed image.
